The use of intelligent digital technology in manufacturing and industrial processes is referred to as “Industry 4.0”. Among the technologies it incorporates are industrial IoT networks, AI, Big Data, robots, and automation. Smart production and the construction of intelligent factories are made possible by Industry 4.0.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is transforming how businesses create, enhance, and distribute their goods. Manufacturers are incorporating new technologies into their operations and manufacturing facilities, such as Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, AI, and machine learning. Advanced sensors, embedded software, and robotics are features of these “smart factories” that collect and analyze data and facilitate better decision-making. When operational data from ERP, supply chain, customer service, and other enterprise systems is coupled with operational data from production operations, even greater value is produced from previously isolated data. Increased automation, predictive maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements, and a new level of efficiency and responsiveness to clients are all results of this digital transformation.
Why is it called Industry 4.0?
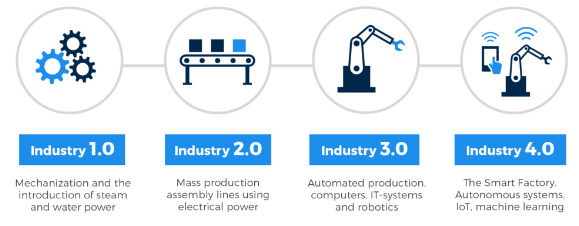
To answer this we will need some historical context, let’s take a look at the previous industrial revolutions.
First Industrial Revolution
Britain experienced the start of the first industrial revolution in the late 18th century. By using water and steam power instead of just human and animal power, it enabled mass production. Machines were used to construct finished things rather of laboriously producing them by hand.
Second Industrial Revolution
Assembly lines and the utilization of gas, oil, and electricity were introduced during the second industrial revolution, which occurred a century later. The introduction of mass production and a certain level of automation to manufacturing processes was made possible by these new power sources and more sophisticated telephone and telegraph communications.
Third Industrial Revolution
Computerization and automation were on the rise during the third industrial revolution. With the emergence of semiconductors, mainframe computing, personal computers, and the internet, it ushered in the digital age.
Fourth Industrial Revolution: Industry 4.0
The fourth industrial revolution, often known as Industry 4.0, is now in effect. Increased automation, the use of intelligent machinery, and smart factories are characteristics of this industry, which makes it possible to create goods more effectively and productively along the entire value chain.
Why Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 transforms manufacturing by incorporating new technologies into production processes. This integration results in increased automation, predictive maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements, and a new level of efficiency and customer responsiveness that was previously unattainable.
Where is Industry 4.0 Applied?
All sorts of industrial businesses, including discrete and process manufacturing, as well as oil and gas, mining, and other industrial areas, can use Industry 4.0 principles and technologies.
When Did Industry 4.0 Begin?
In 2011, as part of a government drive to encourage computerization in manufacturing processes, the phrase “Industry 4.0” was coined in Germany.
How Does Industry 4.0 Work?
Information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) systems merge as a result of Industry 4.0. It establishes communication between larger computer systems and autonomous production equipment.
By incorporating sophisticated digital technologies into manufacturing facilities, Industry 4.0 represents a dramatic change in manufacturing processes. It makes use of IoT networks, AI, Big Data analytics, robotics, automation, and more to enable smart manufacturing. Companies can increase automation, develop predictive maintenance capabilities, boost efficiency, improve decision-making based on real-time data insights, and improve responsiveness to client needs by adopting Industry 4.0 principles.